Car assembly plants often use robots exclusively for spot welding and painting, but there are many other opportunities to use robots throughout the automotive supply chain.
Automotive Manufacturing Robots
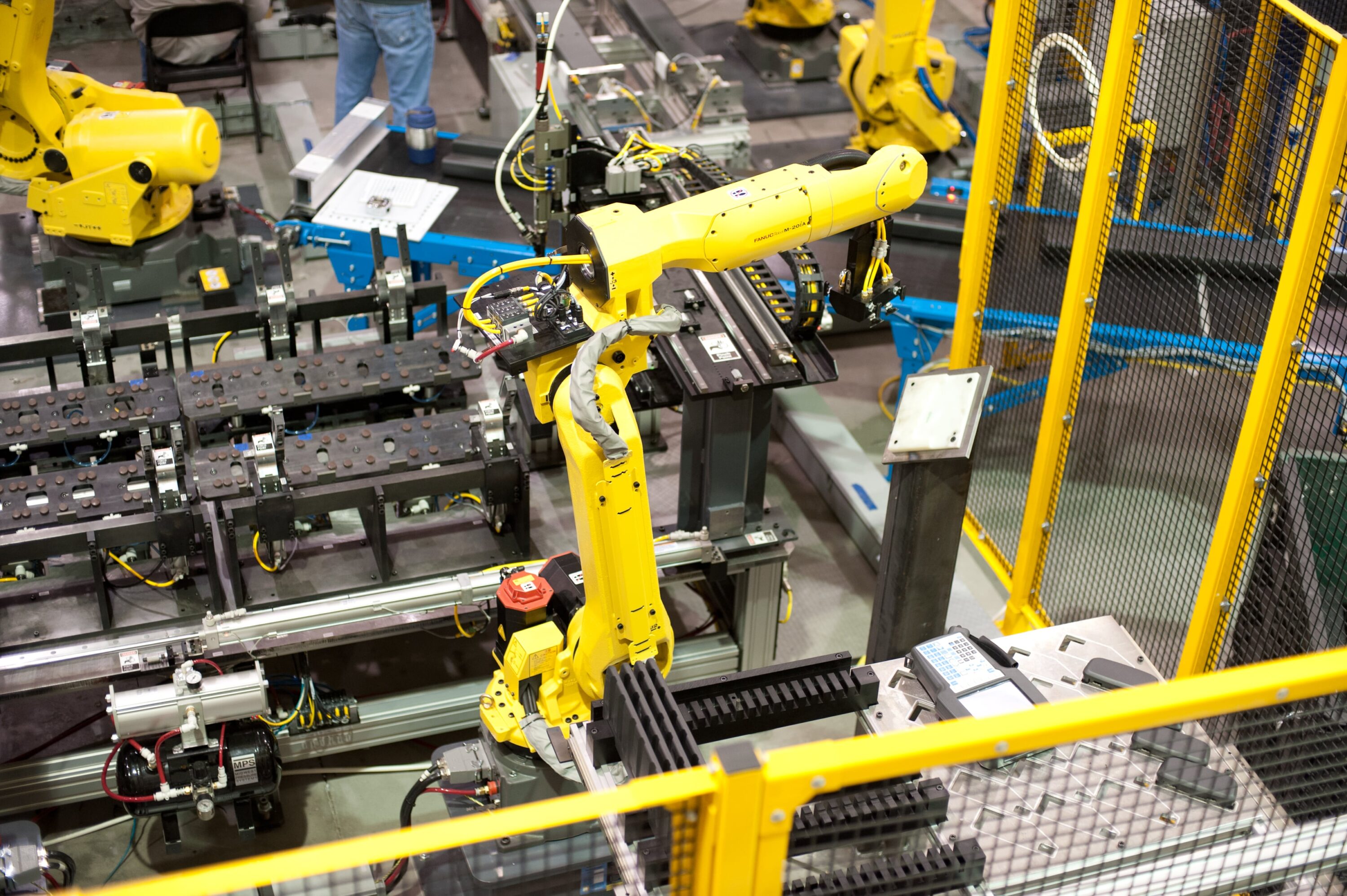
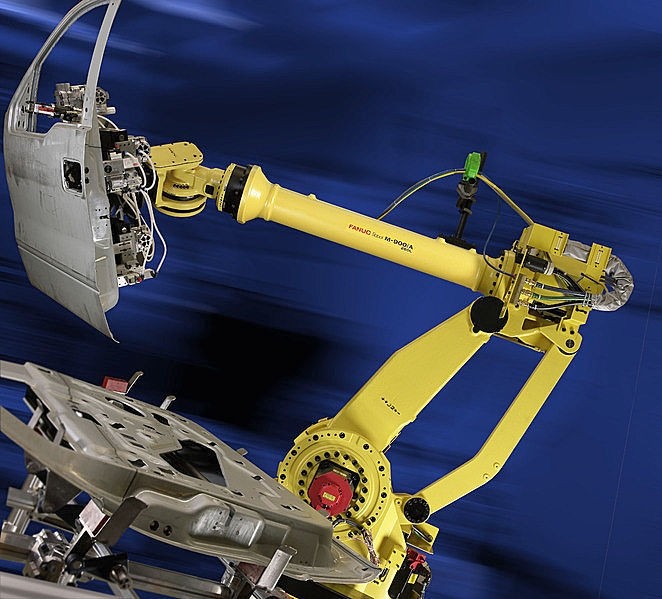

Because of the nature of the automotive industry, products and processes can change quickly. As a leading automotive robotics integrator, Acieta’s automation solutions help car manufacturers stay flexible. Our machines require minimal change over, allowing for redeployment in case of product line obsolescence or other operational changes.
Whether it’s car assembly robots, spot welding different vehicle body styles in quick succession, or a compact machine trimming flash from a range of plastic moldings, robots have the flexibility to switch almost instantly.
Automotive Robotics Applications
There are thousands of parts in every car and truck, and it takes myriad manufacturing processes to make them. Advances in technology for robotics in automotive manufacturing, such as vision systems and force sensing, mean more of these than ever are suitable for robotic automation. Here are some of the best-suited application areas:
WELDING ROBOTS – Large robots with high payload capabilities and long reach can spot weld car body panels; while smaller robots weld subassemblies such as brackets and mounts. Robotic MIG and TIG arc welding position the torch in the same orientation on every cycle, and repeatable speed and arc gap ensure every fabrication is welded to the same high standard. Not only does this ensure higher-quality joints and faster assembly, but it also helps ensure a safe and productive workplace. By taking these often-dangerous tasks off the shoulders of human workers, these automotive manufacturing robots reduce the risk of serious injuries and prevent lost time due to safety incidents.
ROBOTIC ASSEMBLY – Tasks such as screw driving, windshield installation and wheel mounting are all candidates for robotic arms in car manufacturing plants. In many automotive part plants, robots — for example, the high-speed “Delta” machines — are assembling smaller component assemblies such as pumps and motors. One of the key advantages these machines bring to the table is their ability to perform even complex, intricate tasks such with the same level of precision and speed every time. They deliver consistent, replicable results that are so important when it comes to quality assurance.
AUTOMOTIVE MACHINE TENDING – Unloading hot moldings from an injection molding or die casting machine, and loading and unloading CNC machining centers are all good examples of robots tending production machines. In this way, robots serve as important partners to human workers on the production floor. They are capable of handling jobs that are hazardous or challenging for a person, making it possible for the human operators working alongside them to turn their attention to other kinds of work. The result is a more efficient and safer facility where all assets are being used to their fullest effect.
ROBOTIC MATERIAL REMOVAL – Because it can follow a complex path repeatedly, a robot is an ideal tool for light trimming and cutting tasks. Examples include cutting fabrics such as headliners, trimming flash from plastic moldings and die castings, and polishing molds. Force-sensing technology lets the robot maintain constant pressure against a surface in applications like these. When compared to similar work performed by a human being, robotic automation results in less wasted material and overall higher quality in the finished products. The fact that robots can perform the same task thousands of times and produce identical results makes them perfect for this kind of application within an automotive manufacturing facility.
PART TRANSFER ROBOTS – Pouring molten metal in a foundry and transferring a metal stamp from one press to the next are unpleasant jobs for human workers, but they’re ideal tasks for car manufacturing robots. An important aspect of robotic systems that make them superior in these applications is the fact that they never get tired. Human workers can become fatigued over the course of a long workday, which can lead to the quality of their work suffering. A tired or exhausted worker also has a greater risk for injury or mistakes that can lead to dangerous conditions. Offloading physically demanding work to robots can help ensure that their human co-workers remain fresh and alert throughout the day.
Whether you’re in automotive manufacturing or another industry, Acieta’s robotic automation solutions can help your business, identify opportunities and support you through every step of your project. Get started by contacting us today.
To discuss known AUTOMATION OPPORTUNITIES or discover new ones: